This extensive and informative study will fully describe PTFE and PFOA, including their elements leading to their distinctiveness, chemical properties, physical properties, mechanical properties, applications, benefits, and limitations.
Definition
PTFE is a thermoplastic polymer made from tetrafluoroethylene polymerization and is in solid form. At the same time, PFOA is a synthetic chemical generated as part of the fluoropolymers and is in liquid form.
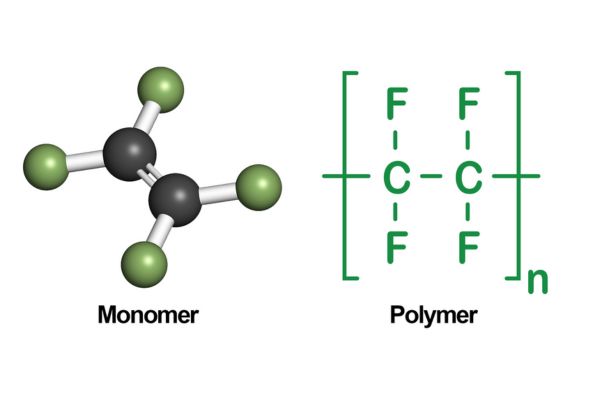

Elements making PTFE and PFOA
Both PTFE and PFOA are made of different elements that make them distinct.
PTFE is made of the following elements:
- Carbon
Each carbon atom is connected to two other carbon atoms in a lengthy chain-like arrangement of carbon atoms.
- Fluorine
PTFE has a lot of fluorine atoms in it.
The carbon chain is encased in a protective sheath of fluorine atoms, resulting in a chemically inert, relatively dense molecule with extremely potent carbon-fluorine interactions.
PFOA is made of the following elements:
- Oxygen
PFOA has two oxygen atoms bonded to carbon atoms.
- Fluorine
PFOA has ten fluorine atoms bonded to carbon atoms.
- Carbon
PFOA has eight carbon atoms.
Physical Properties
The following are the physical properties of PTFE:
- Smooth and non-stick
PTFE has Teflon as a trademark; the fluorine surrounding Teflon’s molecules is the key to its smooth surface. Because of these fluorine atoms, Teflon is resistant to practically all other materials sticking.
- Appearance
It is white and in solid form.
- Density
The density of PTFE is approximately 2200 kg/m3.
- Low friction
The fluorine coating on PTFE contributes to its low coefficient of friction.
- Melting point
It has a high melting point of up to 327 °C
- Electrical insulation
PTFE is not easily porous to electrical energy and can endure high volts without degrading.
- Hydrophobicity
PTFE is water resistant polymer.
The following are the physical properties of PFOA:
- High boiling point
It has a high boiling point of up to 189°C thus can resist high temperatures.
- Appearance
PFOA does not have a distinct color and is in liquid form but may be in gas or solid form under certain conditions.
- Hydrophobic
PFOA is highly hydrophobic because of the fluorocarbon chain hence repels water.
- Melting point
PFOA has a melting point of 67°C
Chemical Properties
Chemical properties of PTFE include:
- Resistant to degradation
Due to the presence of carbon atoms and fluorine, PTFE has excellent resistance to degradation.
- Inertness
PTFE is exceptionally resilient when attacked chemically by bases, acids, and other corrosive chemicals. Most solvents do not affect it, and even potent acids and bases don’t readily react with it.
- Reactivity
PTFE is typically a non-reactive polymer and hence does react with other compounds.
- Chemical resistance
It is very resistant to bases, acids, and caustic chemicals attacking it chemically.
The following are the chemical properties of PFOA:
- Bioaccumulation
PFOA and its compound can build up and are constant in water, soil, birds, and fish hence
- Chemical stability
The chemical stability of PFOA is relatively high hence does not efficiently react with other chemicals in the environment.
Mechanical Properties

Unlike PTFE, PFOA is a synthetic chemical. Its mechanical properties in materials and other compounds may differ depending on the mode of manufacture and the material itself.
The following mechanical properties of PTFE include:
- Tensile strength
It has a high tensile strength of approximately 10-43MPa.
- Elongation
PTFE has a high extension of up to 500%.
- Compressibility
This polymer has low compressibility as a result of its molecular structure.
Under very high temperatures, PTFE cannot change its volume and shape.
- Versatility
Because of its molecular composition, it is adaptable and can flex or bend without deforming.
- Hardness
This polymer has very low hardness as it is soft.

Advantages
The advantages of PTFE and PFOA vary depending on their particular property. The following are the advantages of PTFE as explained:
- Smooth and non-stick
PTFE is very smooth and not sticky hence preferred for non-stick applications such as cookware.
- Resistant to chemicals
PTFE is highly resistant to water, chemicals, bases, acids, solvents, and other corrosive substances.
- Electrical insulation
PFOA is an excellent electrical insulator as it can endure high volt without damage and is not easily permissible to electric energy.
- Low friction surface
PTFE has a very low friction coefficient and is preferred for engineering applications.
- Resistant to high temperatures
PTFE is suitable for use even in high temperatures as it can withstand up to 260°C without damage.
- Resistant to the harsh environment and weather conditions
PTFE can withstand extreme weather conditions and is considered primarily for outdoor applications.
The following are the benefits of PFOA:
- Resistant to high temperatures
Just like PTFE, PFOA can withstand high temperatures without damage.
- Non-stick benefits
This polymer has good non-stick properties and is applied in food processing equipment and cookware.
- Resistant to chemicals
PFOA is highly resistant to bases, acids, and other corrosive compounds.
- Can withstand harsh conditions
PFOA is repellent to environmental factors such as UV radiation.
Disadvantages
Despite PTFE having excellent benefits which make it suitable for its applications, it also has its limitations which include the following:
- Limitation of color options
PTFE is white hence may not be suitable if it’s needed in other color options.
- Cost
PTFE is considerably costly and expensive because of processing and manufacturing.
- Limited high-pressure applications
PTFE is inappropriate for high-pressure applications as its compressive strength is relatively low.
- Bonding difficulty
PTFE has low surface energy and does not quickly bond with other materials.
- Non-decaying
PTFE can stay for very long in the environment without damage or decay because it is non-biodegradable.
The following are the limitations of PFOA as explained:
- Cost
Like PTFE, the processing and manufacturing difficulty makes it more expensive and costly than other materials.
- Limited applications
Due to its properties and environmental risks, PFOA may have limited uses compared to other materials of the same benefit.
- Health risks
PFOA may lead to health problems like cancer and reproductive and immune system disorders.
- Environmental risks
PFOA and its compounds are a risk to the environment as they are considered constant in soil and water and can contaminate the environment.
Applications

The mechanical, physical, and chemical properties of PTFE make it suitable for various applications in the industry.
The following are the applications of PTFE:
- Medical applications
PTFE makes medical implants such as heart patches, replacement ligaments, and vascular garments.
- Electrical and electronics
PTFE makes electrical and electronic components such as circuit boards, electrical insulation, wire insulation, and semiconductor parts.
- Automotive industry
PTFE is used in power steering and transmission, linings for fuel valve stem seals, gaskets, O-rings, and shaft seals.
- Engineering
PTFE makes construction components such as pipe coatings, fittings, bearings, seats and plugs, and valve and pump parts.
- Non-stick coatings
PTFE makes coating surfaces for food processing equipment, bakeware, and cookware.
The following are the applications of PFOA:
- Firefighting foams
PFOA is a byproduct of manufacturing Firefighting foams used in extinguishing fires impacted by flammable liquids.
- Carpeting and textile
PFOA is used in manufacturing carpet and textile treatments that are resistant to dirt and water.
- Non-stick coating
PFOA is applied in making non-stick coatings for bakeware, food processing equipment, and cookware.
Conclusion
PTFE and PFOA are two different chemical compounds with other elements and uses.
PTFE is a synthetic polymer, while PFOA is a synthetic chemical compound that creates other materials.
They have a distinct chemical composition and mechanical, physical, and chemical properties, making them unique for various applications.
PTFE is considerably considered a safe and inert compound compared to PFOA in environmental and health issues.
PTFE is considered a beneficial and adaptable substance with many applications. At the same time, PFOA has health and environmental risks.
More resources:
PTFE Properties -Source: Hansa
PFOA -Source: Wikipedia
PTFE Manufacturing Process – Source: Hansa



