Molding polytetrafluoroethylene requires specialized fabrication techniques due to its unique PTFE properties. For this reason, compression molding PTFE remains a practical and viable option for making stock Teflon parts.
Therefore, this guide explores all fundamental aspects of the Teflon compression molding process.
What is PTFE Compression Molding?
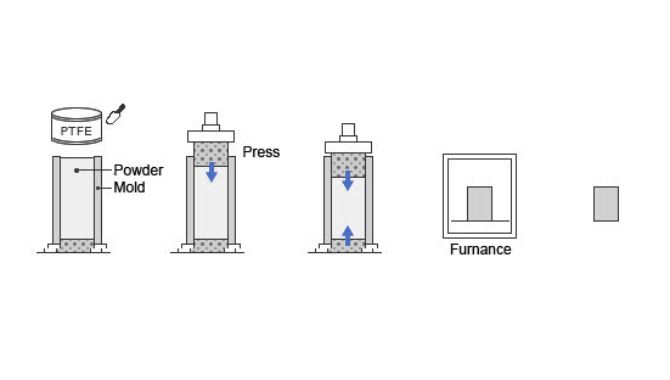
Compression molding PTFE or Teflon involves processing thermoplastic polymer, heating under pressure then subjecting the material to compressive forces to make useful parts.
Through compression molding PTFE, you can make semi-finished or complete products.
You will learn more about the compression molding process shortly.
In most cases, people refer to the PTFE as Teflon. Well, Teflon is DuPont’s brand name.
Advantages of Molded PTFE

There are many reasons why compression molding remains a popular PTFE fabrication process. Some of these reasons are:
- Consistent properties throughout the PTFE structure due to homogenous mixing and fusions
- Cost-effective since it involves few stages and reduces possible PTFE material wastage
- Flexibility when it comes to PTFE molded parts since you can produce many sizes and complex shapes
- Produces PTFE parts with better surface finish
- For PTFE parts manufacturers, using stock Teflon parts can be time-saving
Limitations of Compression Molded PTFE
Although Teflon compression molding has many benefits, it is critical to consider some possible limitations. Among the key issues you should note include;
- When producing molded PTFE stock, the production speed is relatively low.
- Initial high cost of machinery and equipment
Apart from these, compression molding remains a perfect solution for all Teflon molding projects.
Choosing PTFE Material Grades for Compression Molding
Choosing a material for compression molding PTFE parts is critical. Among the key factors you should consider include:
- Cost – virgin PTFE material is more expensive than mechanical-grade PTFE. At the same time, adding more fillers will affect material costs.
- Application – adding fillers or pigment improves certain properties of PTFE. For instance, in case you want to fabricate PTFE parts with anti-static properties, then add graphite. At the same time, graphite will lower the coefficient of friction.
- Material availability – in case a specific PTFE grade is not available, you find an alternative since they share most properties
Having said that, let’s look at some common PTFE grades for the compression molding process:
| PTFE Material Grade | Key Properties |
| Virgin PTFE | · It is 100% pure polytetrafluoroethylene
· Costly · Superior chemical and physical properties |
| Mechanical grade PTFE material | · It is reprocessed PFTE material
· Affordable than virgin PTFE |
| Carbon-filled PTFE | · Superior compressive strength
· Load bearing capacity · Improves static dissipative property |
| Glass-filled PTFE | · Improves durability, and compressive strength
· Makes PTFE less flexible |
| Graphite-filled PTFE | · Lowers coefficient of friction
· Improves thermal and electrical properties · Suitable for anti-static PTFE applications · It is an example of a carbon |
| Molybdenum disulfide-filled PTFE | · Improves stiffness, hardness, and chemical resistance properties |
| Bronze-filled PTFE | · Improved thermal properties
· Reduces cold flow · Improves wear resistance |
| Mica-filled PTFE | · Stabilize the PTFE
· FDA-approved products such as those in the food industry |
Note: You can customize PTFE depending on the requirements of the specific application you want the compression-molded Teflon part to have. The part, PTFE is chemically inert. Therefore, it is compatible with most filler materials.
You can learn about these PTFE material grades here:
PTFE Compression Molding Machine
PTFE compression molding machine can be one set or series of equipment. At a given point, choose an efficient and safe machine.
You can consider these machines for your PTFE molding parts:
- Hydraulic compression press – this machine consists of a molding system. With the help of compressive force and a tooling system, the machine makes PTFE parts conforming to the mold design.
- Sintering equipment – it helps bake/fuse different PTFE particles thereby forming a complete Teflon part.
Of course, you require quality testing equipment and accessories to cut PTFE to size.
Step-by-step PTFE Compression Molding Process
Compression molding is a sequential process, where you have to follow certain steps to get quality PTFE molded parts. Some of the key stages can be summarized as:

Step 1: Preparing PTFE Material
You will choose a suitable PTFE material grade. This will depend on the type of product you want to make.
Go ahead and prepare the material by making homogenous powder.
Step 2: Design Tooling System
The tooling system for PTFE compression molding can either be:
- Single cavity – it is common for small-scale production
- Multi cavity – common design for most high-capacity production processes
You will design the mold to resemble the PTFE components you want to make. In most cases, the mold is made from steel.
During the compression molding Teflon tooling system design, it is important to consider:
- Allowance for shrinkage
- Channels
- Ejection mechanism
- Surface fining of the mold
Step 3: Preforming PTFE Parts
At this stage, you should have both the PTFE material and tooling system ready. Next, pour PTFE powder into the mold, then subject it to reasonable compressive force at room temperature.
When preforming PTFE parts, you can use either:
- Single-axis compression molding – during this process, you will subject PTFE powder to a compression force in one direction. In most cases, you will subject PTFE to vertical compression molding.

- Isostatic compression molding – here, you will subject the PTFE powder to force from nearly all directions. That is, the forces can be horizontal, vertical, or cross-wise directions. Subjecting PTFE powder to these forces simultaneously produces parts with high tensile strength, zero porosity, and better structure.

By the end of this process, you will have a PTFE shape with a shape resembling that of the final product, ready for the next stage.
During preforming PTFE, you will require a pressure magnitude of about 3000 and 4500 pounds per square inch (psi).
Step 4: Sintering PTFE Preform
Sintering PTFE or baking PTFE involves subjecting the material to reasonable head to fusion. Normally, the PTFE sintering temperature is about 685°F to 720°F depending on the Teflon material grade.
During the PTFE sintering process, various powder particles will fuse forming a complete solid section. In most cases, the sintered PTFE will remain in the baking chamber for 1 to 3 days, depending on Teflon material characteristics.
You will allow the sintered PTFE part to cool ready for other processes. You can subject the molded PTFE products to hot coining. That is, using a firing technique while subjecting the cooled PTFE to reasonable pressure, you will improve the quality of the final Teflon components.
In short, compression molding PTFE parts is straightforward and can produce sections with tight tolerance.
Comparing PTFE Injection Molding Process vs. Compression Molding
Although injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process for most rubbers and plastics, it is not suitable for processing PTFE or Teflon. For reason, compression molding Teflon remains a viable and practical PTFE fabrication method.
The reason why injection molding is not suitable for fabricating PTFE is the high melting point. Even above the melting point, which is about 327°C, PTFE has poor flow characteristics. Consequently, injection molding PTFE becomes impossible.
Examples of PTFE Compression Molded Parts
PTFE compression molding produces either finished parts or sections that can use for other processes. Some compression-molded Teflon parts include:
- PTFE molded rods
- PTFE molded tubes
- Molded PTFE sheet
- Molded PTFE pipes
- Molded PTFE plates, etc.
You can process the products further to make different PTFE parts. There are thousands of PTFE parts.
Let’s mention a few:
| PTFE Properties for Specific Applications | Examples of Applications after PTFE Compression Molding |
| Low coefficient of friction | · Ball bearings
· Bushing · Guide rails |
| Chemically inert | · Piping systems in the chemical industry |
| Resistance to temperature (low and high) | · Sealing applications such as gaskets, O-rings, etc
· Bearings |
| Electrical insulation | · PTFE cable sheathing |
| Non-stick property | · PTFE tubes in 3D printers |
| Safety and FDA Approval | ·Tube pharmaceutical machines
· Tubes for clean room processing |
You can learn more about Teflon/PTFE parts.
Conclusion
As you can see, PTFE compression molding plays a critical role in Teflon parts manufacturing. For a successful PTFE molding process, you should necessary equipment, choose quality material and know the specific requirements for the parts you want to produce.
For all your PTFE molded parts, HANSA is your trusted partner – contact us now.



