
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy alkane) are copolymers of tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoroethers required for devices exposed to harsh biological and chemical elements.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a fluoropolymer containing fluorine and carbon atoms. It is known for its resistance to chemicals and micro porous nature making it water repellent
PFA VS PTFE History
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): It was discovered in 1938 by an American chemist Roy J. Plunkett at Du Pont Company. He was in charge of looking after a specific tetrafluoroethylene sample. An accidental discovery was found as he was attempting to create a high quality coolant gas. The sample was taken out and they found out a waxy white texture coating due to the gas polymerizing. This material has been used many years.

Perfluoroalkoxy alkaline (PFA: It was made to cover PTFE limitations like their differences in melting points.
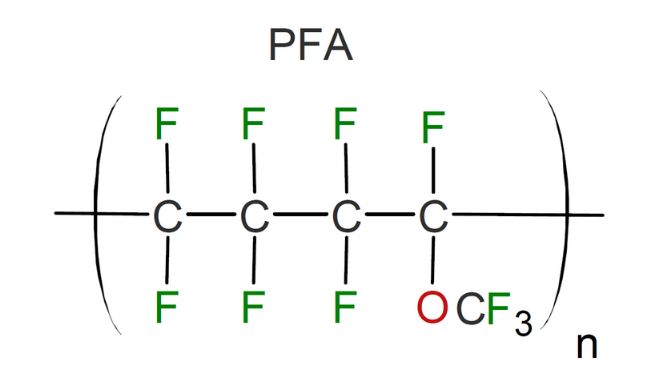
Comparing PFA and PTFE Properties
PFA Properties
PFA material is known for non-flammable, high chemical resistance, low coefficient of friction, high purity, high dielectric strength and Low moisture absorption
PTFE Properties
PTFE is popular for its high density at 2200kg/m3, high electrical resistance and dielectric strength, hydrophobic nature, intense flexural strength and low friction coefficient.
PFA Vs. PTFE Advantages
PFA Advantages
- Transparency form making it ideal for making laboratory equipment
- It is easy to re-mould and weld
- Highly chemical resistance
- Exceptional resistance to high temperature
- High purity levels
PTFE Advantages
- Non-stick properties
- High chemical resistance
- Easy to install PTFE liner
- Corrosive resistant
- Non flammable
PFA and PTFE Disadvantages
Although these materials have superior properties in modern applications, they have certain limitations. These limitations include:
PFA Disadvantages
- Low flex durability compared to PTFE
- Low permeation
- Expensive compared to PTFE
PTFE Disadvantages
- Can revert to its original shape after installed
- It is not easy to manufacture in large quantities
- Material not easily weldable
Applications: PFA and PTFE
Some common practical applications of these materials include:
PFA Applications

It is used to make laboratory and medical plastic equipment because it can withstand chemical corrosion. Additionally, it can act as sheet lining for chemical containers.
Other applications include tubing for fluid passage like pipelines and extreme temperature uses. More importantly, it is a perfect choice where high purity is a priority.
PTFE Applications
It is used to make nonstick cooking pans due to its hydrophobic and non-stick properties. Where you wish to reduce friction, PTFE coating or material is always a perfect alternative.
Due to its chemically inert properties, it is used in tanks that store reactive fluids. Remember, PTFE is highly non-reactive due to its inertness from fluorine atoms.
Conclusion
With this information, you can choose whether to choose PFA or PTFE for any applications. For all you PTFE products, HANSA is here to help.



