
Teflon ist ein thermoplastisches Polymer, das durch Tetrafluorethylen-Polymerisation hergestellt wird und in fester Form vorliegt.
Es gibt verschiedene Arten von Teflon: PTFE, FEP, ETFE, Und PVDF.
Die Chemikalie PTFE ist im Handel als Teflon bekannt und wird von der DuPont Company hergestellt.
Durch die Polymerisation von Tetrafluorethylen entstehen die thermoplastischen Polymere Teflon und PTFE, die in fester Form vorliegen.
Daher ist PTFE der wissenschaftliche Name und Teflon der Markenname für dasselbe Material.

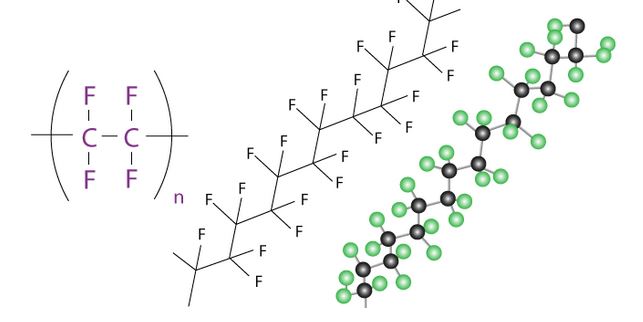
Elemente zur Herstellung von PTFE und Teflon
PTFE und Teflon haben das gleiche chemische Element, da sie sich auf das gleiche Material beziehen.
PTFE und Teflon bestehen aus folgenden Elementen:
Fluor
Teflon und PTFE enthalten viele Fluoratome.
Die Kohlenstoffkette ist von einer Schutzhülle aus Fluoratomen umgeben, wodurch ein chemisch inertes, relativ dichtes Molekül mit extrem starken Kohlenstoff-Fluor-Wechselwirkungen entsteht.
Kohlenstoff
Jedes Kohlenstoffatom ist mit zwei anderen Kohlenstoffatomen in einer langen kettenartigen Anordnung von Kohlenstoffatomen verbunden.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
Da Teflon und PTFE dasselbe Material bedeuten, sind ihre physikalischen Eigenschaften wie folgt:
- Aussehen
Beide Polymere sind weiß und liegen in fester Form vor.
- Dichte
Die Dichte von PTFE und Teflon beträgt ca. 2200 kg/m3.
- Glatt und antihaftbeschichtet
PTFE und Teflon haben aufgrund des Fluors, das ihre Moleküle umgibt, glatte Oberflächen. Dank dieser Fluoratome widerstehen Teflon und PTFE dem Anhaften praktisch aller anderen Materialien.
- Geringe Reibung
Ihr niedriger Reibungskoeffizient wird durch die Fluorbeschichtung der beiden Polymere erreicht.
- Schmelzpunkt
Sie haben einen hohen Schmelzpunkt von bis zu 327 °C
- Elektrische Isolierung
PTFE und Teflon reagieren nicht so leicht porös auf elektrische Energie und können hohen Spannungen standhalten, ohne Schaden zu nehmen.
- Hydrophobie
Es handelt sich um wasserbeständige Polymere.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Die chemischen Eigenschaften von PTFE und Teflon sind ähnlich. Dazu gehören die folgenden:
- Trägheit
PTFE und Teflon sind außergewöhnlich widerstandsfähig gegenüber chemischen Angriffen durch Basen, Säuren und andere ätzende Chemikalien.
Die meisten Lösungsmittel haben keine Auswirkungen auf sie und selbst starke Säuren und Basen reagieren nicht so leicht mit ihnen.
- Beständig gegen Abbau
Aufgrund der Anwesenheit von Kohlenstoffatomen und Fluor verfügen PTFE und Teflon über eine ausgezeichnete Beständigkeit gegen Abbau.
- Reaktivität
Diese Polymere sind normalerweise nicht reaktiv und reagieren daher mit anderen Verbindungen.
- Chemische Beständigkeit
Sie sind sehr widerstandsfähig gegen chemische Angriffe durch Basen, Säuren und ätzende Chemikalien.
Mechanische Eigenschaften

Teflon und PTFE weisen ähnliche mechanische Eigenschaften auf, darunter die folgenden:
- Verlängerung
PTFE und Teflon haben eine hohe Dehnung von bis zu 500%.
- Kompressibilität
Aufgrund ihrer Molekülstruktur weisen diese Polymere eine geringe Kompressibilität auf.
Bei sehr hohen Temperaturen können PTFE und Teflon ihr Volumen und ihre Form nicht verändern.
- Zugfestigkeit
Sie haben eine hohe Zugfestigkeit von etwa 10–43 MPa.
- Vielseitigkeit
Aufgrund ihrer molekularen Zusammensetzung sind sie anpassungsfähig und können sich biegen oder krümmen, ohne sich zu verformen.
- Härte
Diese Polymere haben eine sehr geringe Härte, da sie weich sind.
Vorteile
Die besonderen Eigenschaften von Teflon und PTFE bestimmen ihre Vorteile und werden für ihre verschiedenen Anwendungen berücksichtigt.
Die Vorteile von PTFE und Teflon sind:
- Beständig gegen Chemikalien
Sie sind äußerst beständig gegen Wasser, Lösungsmittel, Basen, Säuren, Chemikalien und andere ätzende Substanzen.
- Elektrische Isolierung
PFOA ist ebenso wie Teflon ein hervorragender elektrischer Isolator, da es hohe Spannungen ohne Schaden aushält und elektrische Energie nicht so leicht abgibt.
- Antihaftbeschichtet und glatt
Sie sind sehr glatt und nicht klebrig und werden daher bevorzugt für Antihaftanwendungen wie Kochgeschirr verwendet.
- Oberfläche mit geringer Reibung
Beide haben einen sehr niedrigen Reibungskoeffizienten und werden für technische Anwendungen bevorzugt.
- Beständig gegen hohe Temperaturen
Sie eignen sich für den Einsatz auch bei hohen Temperaturen, da sie bis zu 260°C unbeschadet überstehen.
- Beständig gegen raue Umgebungs- und Wetterbedingungen
Die Polymere halten extremen Witterungsbedingungen stand und kommen vor allem für den Einsatz im Außenbereich in Frage.
Nachteile
Obwohl PTFE und Teflon hervorragende Vorteile aufweisen, die sie für ihre Anwendungen geeignet machen, unterliegen sie auch Einschränkungen, darunter die folgenden:
- Kosten
Aufgrund der Verarbeitungs- und Herstellungskosten sind Polymere sehr kostspielig.
- Eingeschränkte Hochdruckanwendungen
Für Hochdruckanwendungen sind sie ungeeignet, da ihre Druckfestigkeit relativ gering ist.
- Nicht verrottend
Sie können sehr lange in der Umwelt verbleiben, ohne Schaden zu nehmen oder zu verrotten, da sie nicht biologisch abbaubar sind.
- Bindungsschwierigkeiten
Teflon und PTFE haben eine geringe Oberflächenenergie und verbinden sich nicht so schnell mit anderen Materialien.
- Einschränkung der Farboptionen
Sie sind weiß und daher möglicherweise nicht geeignet, wenn sie in anderen Farboptionen benötigt werden.
Anwendungen
Aufgrund ihrer mechanischen, physikalischen und chemischen Eigenschaften eignen sich PTFE und Teflon für zahlreiche Anwendungen in der Industrie.
Die Anwendungsgebiete von PTFE und Teflon sind:
- Automobilindustrie
Sie werden in Servolenkungen und Getrieben, Auskleidungen für Kraftstoffventilschaftdichtungen, Dichtungen, O-Ringen und Wellendichtungen verwendet.
- Maschinenbau
Sie werden in Konstruktionskomponenten wie Rohrbeschichtungen, Armaturen, Lagern, Sitzen und Stopfen sowie Ventil- und Pumpenteilen verwendet.
- Elektrik und Elektronik
Sie werden zur Herstellung elektrischer und elektronischer Komponenten wie Leiterplatten, elektrischer Isolierung, Drahtisolierung und Halbleiter verwendet.
- Medizinische Anwendungen
Polymere werden zur Herstellung medizinischer Implantate wie Herzpflastern, Ersatzbändern und Gefäßbekleidung verwendet.
- Antihaftbeschichtungen
Oberflächen von Kochgeschirr, Backformen und Geräten zur Lebensmittelverarbeitung werden mit PTFE und Teflon beschichtet.
Abschluss
PTFE und Teflon sind die gleichen chemischen Verbindungen oder Materialien.
Beide sind synthetische Polymere mit der gleichen chemischen Zusammensetzung und den gleichen physikalischen, mechanischen und chemischen Eigenschaften.
Der Unterschied zwischen den beiden besteht darin, dass Teflon der Markenname für PTFE ist, der einem Unternehmen namens DuPont gehört.
Weitere Ressourcen:
PTFE-Anwendungen – Quelle: HANSA
Teflon – Quelle: Wikipedia
PTFE-Herstellungsprozess – Quelle: HANSA
Gefülltes PTFE – Quelle: HANSA



