Although both FEP and PTFE are fluoropolymers, they differ in their properties and corresponding applications. When making a purchase, you should choose the best material based on the intended application. Below, I will explain the differences between FEP and PTFE to help you avoid unnecessary problems caused by using the wrong material.
Chemical Structure
The chemical formula of PTFE is -CF2-CF2-, with each carbon atom bonded to two fluorine atoms. PTFE has a completely linear structure, with the molecular chains arranged neatly in a helical shape. The chemical formula of FEP is-[CF2-CF2]m-[CF2-CF(CF3)]n-, and it is composed of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) and hexafluoropropylene (HFP). More precisely, FEP is a fluorinated ethylene propylene copolymer. HFP breaks the original completely linear structure of PTFE by introducing a -CF(CF3)- side chain. This change also affects the properties of the FEP material, which I will explain in detail below.
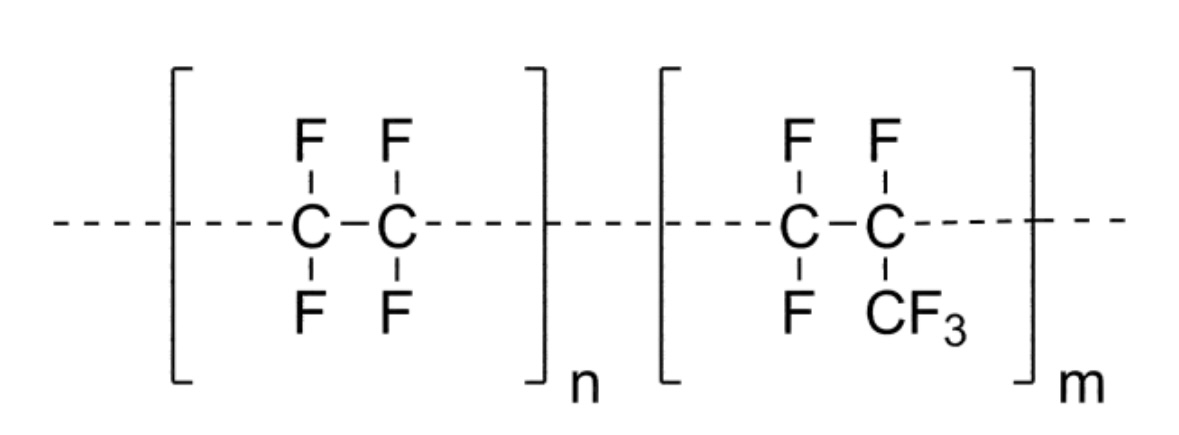
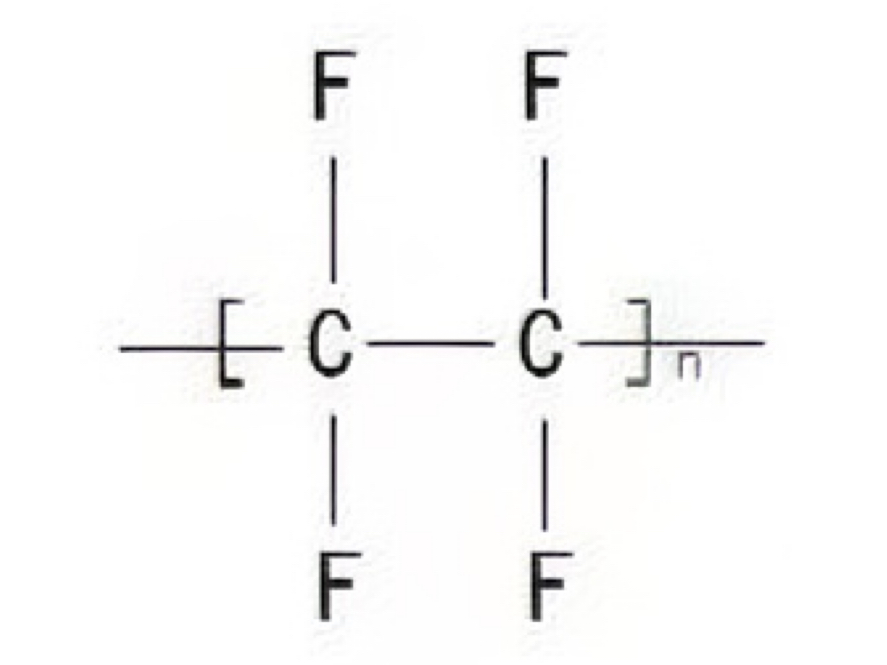
Comparison of The Properties of FEP and PTFE
Chemical Resistant
Both PTFE and FEP have stable chemical properties and are resistant to chemical corrosion. This is due to the high bond energy of their carbon-fluorine bonds, and the protection provided by the two fluorine atoms surrounding the carbon backbone. However, under high temperatures, in the presence of corrosive chemicals, or in humid environments, PTFE exhibits slightly better chemical stability than FEP. In practical applications, however, the difference between the two is very small and almost negligible.
Processability
PTFE is a thermosetting plastic with a highly regular molecular structure, resulting in an extremely high melting point of approximately 327°C. Therefore, it is difficult to process. Traditional melt processing methods are unsuitable because it is difficult to melt at high temperatures; PTFE can only be processed and molded through sintering. FEP, on the other hand, is a thermoplastic material. Its HFP side chains disrupt the regularity of the original molecular chain, lowering the melting point to 260°C. This significantly reduces processing difficulty, allowing it to be processed using traditional injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming techniques.
Temperature Range
PTFE can withstand extreme temperatures, boasting a wide temperature range with a continuous operating temperature of -200 to 260℃ (-328 to 500℉), while also maintaining excellent chemical stability. FEP has slightly lower temperature resistance than PTFE, with a temperature range of -200 to 200℃ (-328 to 392℉).
Resistência mecânica
The tensile strength of PTFE is 20-30 MPa.
The tensile strength of FEP is 15-25 MPa.
Flexibilidade
FEP is significantly more flexible than PTFE. This difference primarily stems from the chemical structure of the two materials. PTFE has a regular and orderly molecular chain structure with a high degree of crystallinity, ranging from 60-80%. Crystallinity refers to the percentage of the crystalline portion of a polymer material relative to its total volume. FEP, on the other hand, has a lower degree of crystallinity (only 50-50%) due to the influence of its extra side chains. Therefore, FEP is much softer than PTFE, making it easier to install and use in confined spaces.
Isolamento elétrico
Both PTFE and FEP have excellent electrical insulation properties, and both are considered super-insulating materials.
Transparency
Transparency is one of the most significant differences between FEP and PTFE. FEP is much more transparent than PTFE, mainly due to their molecular structures. PTFE has a high degree of crystallinity, and light is scattered at the interface between crystalline and amorphous regions. The scattered light appears milky white or translucent, making PTFE appear opaque. FEP, on the other hand, has a lower degree of crystallinity, resulting in very little scattering of light at the interface between crystalline and amorphous regions. Light can pass through, making FEP appear transparent. Even when PTFE is made into a thin film, it only achieves limited light transmission. FEP can be manufactured into highly transparent products.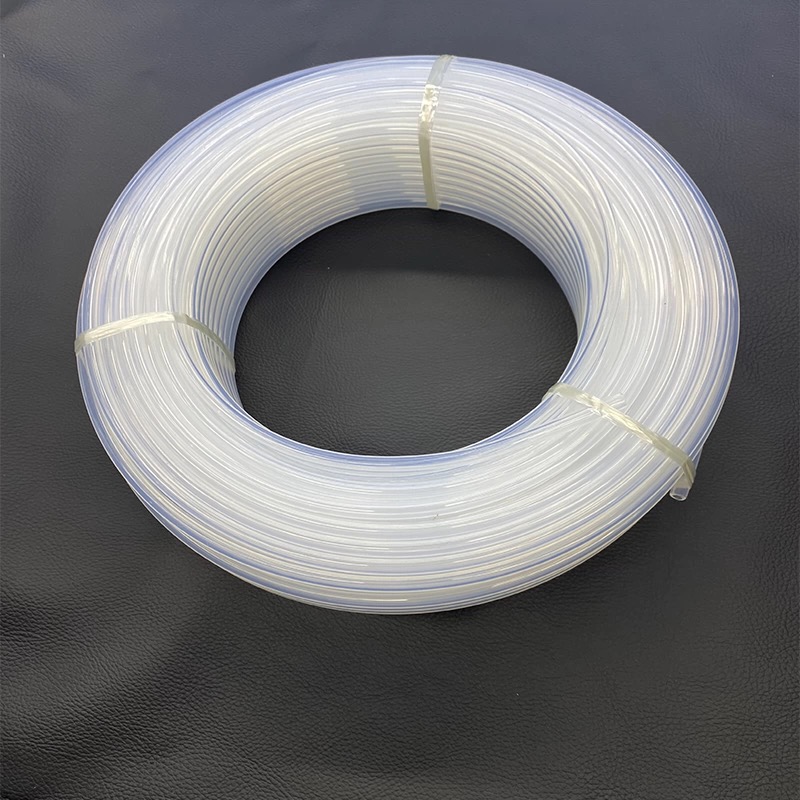
Making The Best Choice Between FEP and PTFE
If you want to choose the most suitable material for your application, you should make your decision based on their performance characteristics. If you still can’t decide after comparing the above characteristics, then I will provide you with more detailed and specific recommendations.
Based on the differences in the properties of FEP and PTFE, their different application areas can be distinguished:
-
Pipes and pipe fittings
The advantages of PTFE are its corrosion resistance, chemical stability, and certain rigidity.
Therefore, in semiconductor applications, PTFE can be used to transport ultrapure water and high-purity chemicals; in laboratories, it can transport various corrosive liquids; and in the medical field, it can be used to transport drugs and reagents.
The advantages of FEP are its transparency and good flexibility.
Therefore, in the food processing industry, FEP allows for easy observation of the fluid state while transporting liquids; and in the chemical industry, it is used for connecting equipment.
-
Isolamento elétrico
Both PTFE and FEP have excellent insulation properties, but PTFE can be used under more extreme conditions, and its low dielectric loss makes it ideal for microwave and radar applications.
High-frequency communication in aerospace and satellite electronic equipment also commonly uses PTFE as an insulating material.
The advantages of FEP lie in its high flexibility, ease of processing, and low cost. It is suitable for general insulation applications.
For example, household appliances, automotive insulation, general industrial insulation, and cables that require frequent bending.
-
Coatings, Linings:
PTFE’s chemical resistance makes it ideal for reactor linings in industrial applications, its low friction is used for coatings on anti-friction components in machinery, and its high-temperature resistance allows it to be used as a coating for the inner walls of high-temperature furnaces.
FEP, due to its three advantages of transparency, flexibility, and solubility, is used as a coating for observation windows in the food processing industry; in the medical field, it is used as a coating for medical devices. Because of its solubility, it can be repeatedly applied and repaired.
Important Considerations
-
Extreme Environments
PTFE is more suitable than FEP for applications in extreme environments, such as highly corrosive environments and high-temperature environments exceeding 200℃, where FEP cannot be used.
-
Flexibilidade
In applications requiring frequent bending or folding, your first choice should be FEP, as it is more flexible than PTFE.
-
Transparency
If you need to observe the internal environment, you should use a highly transparent material like FEP, which allows light to pass through, rather than PTFE, which has a milky white surface.
-
Processability
FEP is much easier to process than PTFE. If you need to manufacture products with complex shapes, choose FEP. If you need mass production, and the application is not under extremely harsh conditions, you should also choose FEP. This will help reduce your costs.
Conclusão
In summary, the differences between FEP and PTFE lie in four aspects: temperature resistance, flexibility, transparency, and processability. Above, I have explained the differences between the two from the perspectives of their chemical structure, properties, and applications. If you still have any questions, please contact us, and we will patiently and thoroughly answer them for you. Of course, if you need to order related products, we will offer you our best price and service. Please trust Hansa; we are a manufacturer specializing in PTFE and other fluoroplastics, with 25 years of production and sales experience. We believe our cooperation will be of great benefit to you!
Perguntas frequentes
What is the difference between Teflon and FEP?
Teflon is simply PTFE, but it’s a registered trademark of PTFE, owned by DuPont. The difference between them is what I described above.
Which is more expensive, FEP or PTFE?
Overall, FEP is actually more expensive than PTFE. This is because FEP is more easily processed, can be melt-processed, and has a more complex manufacturing process. Furthermore, it is transparent and flexible, giving it a wider range of applications. Currently, the lowest market price for FEP is $6.14/kg, while the lowest price for PTFE is $5.65/kg.
FEP vs PTFE coefficient of friction
PTFE has a lower coefficient of friction than FEP. The static coefficient of friction for PTFE is 0.04-0.05, and the dynamic coefficient of friction is 0.04-0.07, sometimes even as low as 0.01, while the static coefficient of friction for FEP is 0.05-0.07, and the dynamic coefficient of friction is 0.05-0.09.
FEP vs PTFE vs PFA
FEP, PTFE, and PFA are all fluoropolymers, but they have significant differences in structure and properties. Their temperature resistance is PTFE > PFA > FEP. Both FEP and PFA can be processed by melt processing, but PTFE can only be processed by sintering. Transparency is FEP > PFA > PTFE. The coefficient of friction is PTFE < PFA < FEP. Chemical resistance is PTFE > PFA > FEP. Price is PFA > FEP > PTFE.



